A drag count is a single unit of drag as defined by aerospace engineers. Drag is generally computed using the equation:
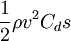
Where:
- ρ is the air density
- v is the current airspeed
- Cd is the drag coefficient (a dimensionless constant, usually on the order of 0.02 to 0.04 for an aircraft in cruise)
- s is the aircraft wing area
A drag count is 1/10000 of a Cd. So if, for example, the steady state drag coefficient is 0.0200 and someone sticks a hand out the window adding 5 drag counts, the new drag coefficient would be:
- 0.0200 + 0.0005 = 0.0205 or 205 drag counts.
Drag count is used as a crude measure for the change in drag coefficient (it is not a direct measure of drag as it is associated with a reference area, it is only valid for use as a relative assessment of change).